As environmental awareness rises, conserving energy is vital for protecting the planet and cutting electricity costs. Energy Saving Devices, such as smart thermostats and LED bulbs, enhance efficiency and minimize energy waste. But do they truly deliver? This article explores how they function, reviews evidence of their effectiveness, and outlines potential drawbacks.

How Energy Saving Devices Function
Energy saving devices are designed to optimize power usage. Many of these products function by:
• Using efficient technology: Devices like LED bulbs and energy-efficient appliances are built to consume less power while delivering the same performance.
Smart sensors and connectivity enhance energy efficiency: Smart thermostats adjust heating or cooling to match your schedule, lowering energy use when you’re away. Similarly, smart power strips cut power to idle devices, eliminating “phantom loads.”
• Harnessing renewable sources: Some devices, like solar inverters and EV charging stations, integrate renewable energy into the mix, complementing traditional power usage with greener alternatives.
The Science Behind Energy Saving Devices
Years of research and real-world testing have demonstrated that energy saving devices can substantially cut power consumption. For instance:
• LED lighting uses a fraction of the energy required for incandescent lighting while lasting significantly longer. Studies from energy authorities confirm that retrofitting buildings with LED bulbs can lead to noticeable savings.
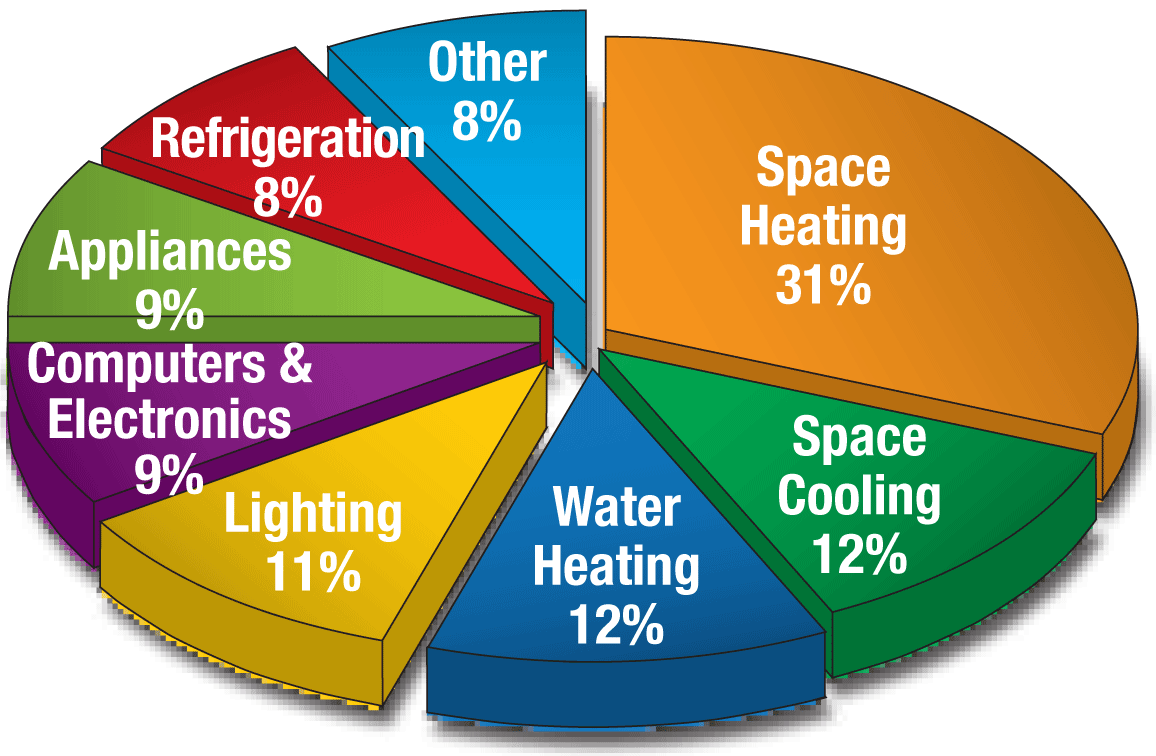
Smart thermostats cut heating and cooling costs by adapting to occupant habits and adjusting temperatures. User case studies show energy reductions of 10-15% for climate control systems.
• Power management systems in devices and appliances help reduce the energy wasted on standby circuits, making homes and offices more efficient—especially when numerous devices are in operation.
Supporting Evidence
Numerous studies, pilot programs, and testimonials highlight the effectiveness of energy saving devices. Businesses report notable savings through integrated EV charging and solar-enhanced systems. Real-world applications consistently show that incorporating these devices into energy management systems yields both immediate and lasting results.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
However, it’s important to be aware of the potential limitations:
• Initial Cost: Many energy saving devices come with a higher upfront price. While the long-term savings often justify the investment, the initial expense can be a barrier for some consumers.
• Installation and Compatibility: Not every home or business setup will support a seamless integration of all energy saving technologies. Retrofitting older systems may require professional installation and compatibility checks.
• Variable Results: The effectiveness of these devices can vary depending on usage patterns, device quality, and environmental factors. Some systems work better in specific climates or settings while showing limited benefits in others.
Conclusion
Do energy saving devices really work? The answer is yes—when users apply them correctly, integrate them effectively, and set realistic expectations. These devices help lower costs and reduce your carbon footprint. By evaluating your energy needs carefully and choosing high-quality, compatible products, you can use modern technology to make your home or business more efficient.






Leave a Reply